前言
A*算法是常用的游戏算法之一,也是初学者比较难掌握的一个算法。
本文在Unity中以GUI的方式形象的再现了A*算法的详细步骤,
包括地图的搜索、FGH的计算以及开启关闭列表的变化等。
博文首发地址:http://blog.csdn.net/duzixi
步骤一:
创建Unity新工程新场景
步骤二:
创建AStar.cs脚本,将以下代码内容粘贴覆盖后,保存运行即可
/// <summary>
/// A*算法 Unity GUI实现
/// Created by 杜子兮(duzixi.com) 2015.2.19
/// www.lanou3g.com All Rights Reserved
/// </summary>
using UnityEngine;
using System.Collections;
using System; // 用到排序接口
// 枚举:定义格子类型
public enum GridType {
Normal, // 常规
Obstacle, // 障碍
Start, // 起点
End // 终点
}
// 定义格子类(继承可比较接口 IComparable)
public class Grid : IComparable{
public int x; // x 坐标
public int y; // y 坐标
public int F; // 总评分
public int G; // 从起点到当前点的消耗值
public int H; // 从当前点到终点的估算值(直走10,斜走14)
public GridType gridType; // 格子类型
public Grid fatherNode;
// 可比较接口的实现(用于排序)
public int CompareTo (object obj)
{
Grid g1 = (Grid) obj; // 强制类型转换
if (this.F < g1.F) // 升序
return -1;
if (this.F > g1.F) // 降序
return 1;
return 0; // 相等
}
}
// A*算法
public class AStar : MonoBehaviour {
private const int col = 7; // 列数
private const int row = 5; // 行数
private int size = 70; // 大小
private Grid[,] map; // 地图(格子二维数组)
private const int xStart = 2;
private const int yStart = 1;
private const int xEnd = 2;
private const int yEnd = 5;
ArrayList openList; // 开启列表(重要!!)
ArrayList closeList; // 关闭列表(重要!!)
// 初始化
void Start () {
map = new Grid[row, col]; // 创建地图
for (int i = 0; i < row; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < col; j++) {
map[i,j] = new Grid(); // 实例化格子
map[i,j].x = i; // x坐标赋值
map[i,j].y = j; // y坐标赋值
}
}
map[xStart, yStart].gridType = GridType.Start; // 确定开始位置
map[xStart, yStart].H = Manhattan(xEnd, yEnd); // 初始化开始位置的H值
map[xEnd, yEnd].gridType = GridType.End; // 确定结束位置
for (int i = 1; i <= 3; i++) { // 确定障碍位置
map[i, 3].gridType = GridType.Obstacle;
}
openList = new ArrayList(); // 初始化开启列表
openList.Add(map[xStart, yStart]); // 将开始节点放入开放列表中
closeList = new ArrayList(); // 初始化关闭列表
}
void OnGUI() {
// 绘制地图
for (int i = 0; i < row; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < col; j++) {
// 根据格子类型设置背景颜色
Color bgColor;
if (map [i, j].gridType == GridType.Start) {
bgColor = Color.green;
} else if (map [i, j].gridType == GridType.End) {
bgColor = Color.red;
} else if (map [i, j].gridType == GridType.Obstacle) {
bgColor = Color.blue;
} else if (closeList.Contains (map [i, j])) {
bgColor = Color.black;
} else {
bgColor = Color.gray;
}
GUI.backgroundColor = bgColor;
// 用按钮表示格子
GUI.Button(new Rect(j * size, i * size, size, size), FGH (map[i, j]));
}
}
if (GUI.Button(new Rect(col * size, 0 , size, size), "Go Next")) {
NextStep();
}
// 绘制开启列表
for (int j = 0; j < openList.Count; j++) {
GUI.Button(new Rect(j * size, (row + 1) * size, size, size), FGH((Grid)openList[j]));
}
// 绘制关闭列表
for (int j = 0; j < closeList.Count; j++) {
GUI.Button(new Rect(j * size, (row + 2) * size, size, size), FGH((Grid)closeList[j]));
}
}
// 通过逆向追溯找到路径
void showFatherNode(Grid grid) {
if (grid.fatherNode != null) {
print (grid.fatherNode.x + "," + grid.fatherNode.y);
showFatherNode(grid.fatherNode);
}
}
// 走下一步
void NextStep() {
// 0. 只要开启列表有节点, 就进行下一个过程
if (openList.Count == 0) {
print ("Over !");
return;
}
// 1. 从开放列表中选择第一个节点并将其作为当前节点
Grid grid = (Grid)openList[0];
if (grid.gridType == GridType.End) {
showFatherNode(grid);
print ("Over !");
return;
}
// 2. 获得这个当前节点不是障碍物的邻近节点
for (int m = -1; m <= 1; m++) {
for (int n = -1; n <= 1; n++) {
if ( !( m == 0 && n == 0 )) {
int x = grid.x + m;
int y = grid.y + n;
// 3. 对于每一个邻近节点,查看是否已在关闭列表中.
if (x >= 0 && x < row && y >= 0 && y < col &&
map[x,y].gridType != GridType.Obstacle &&
!closeList.Contains(map[x, y]) ) {
// 4.如果不在, 计算所有F、H、G
int g = grid.G + (int)(Mathf.Sqrt(Mathf.Abs(m) + Mathf.Abs(n)) * 10);
if (map[x, y].G == 0 || g < map[x, y].G) {
map [x, y].G = g;
}
map[x, y].H = Manhattan(x, y);
map[x, y].F = map[x, y].G + map[x, y].H;
// 5.将代价数据存储在邻近节点中,并且将当前节点保存为该邻近节点的父节点.
// 最后我们将使用这个父节点数据来追踪实际路径.
map[x, y].fatherNode = grid;
// 6.将邻近节点存储在开放列表中.
if (!openList.Contains(map[x, y])) {
openList.Add(map[x, y]);
}
// 7.根据F,以升序排列开放列表.
openList.Sort();
}
}
}
}
// 8. 如果没有邻近节点需要处理, 将当前节点放入关闭列表并将其从开放列表中移除.
closeList.Add(grid);
openList.Remove(grid);
}
// H值(曼哈顿估算法)
int Manhattan(int x, int y) {
return (int)(Mathf.Abs(xEnd - x) + Mathf.Abs(yEnd - y)) * 10;
}
// 将格子FGH 以字符串形式显示
string FGH(Grid grid) {
string fgh = "F:" + grid.F + "\n";
fgh += "G:" + grid.G + "\n";
fgh += "H:" + grid.H + "\n";
fgh += "(" + grid.x + "," + grid.y + ")";
return fgh;
}
}
步骤三:
点击画面上的“Go Next”按钮,即可观察每部计算详情
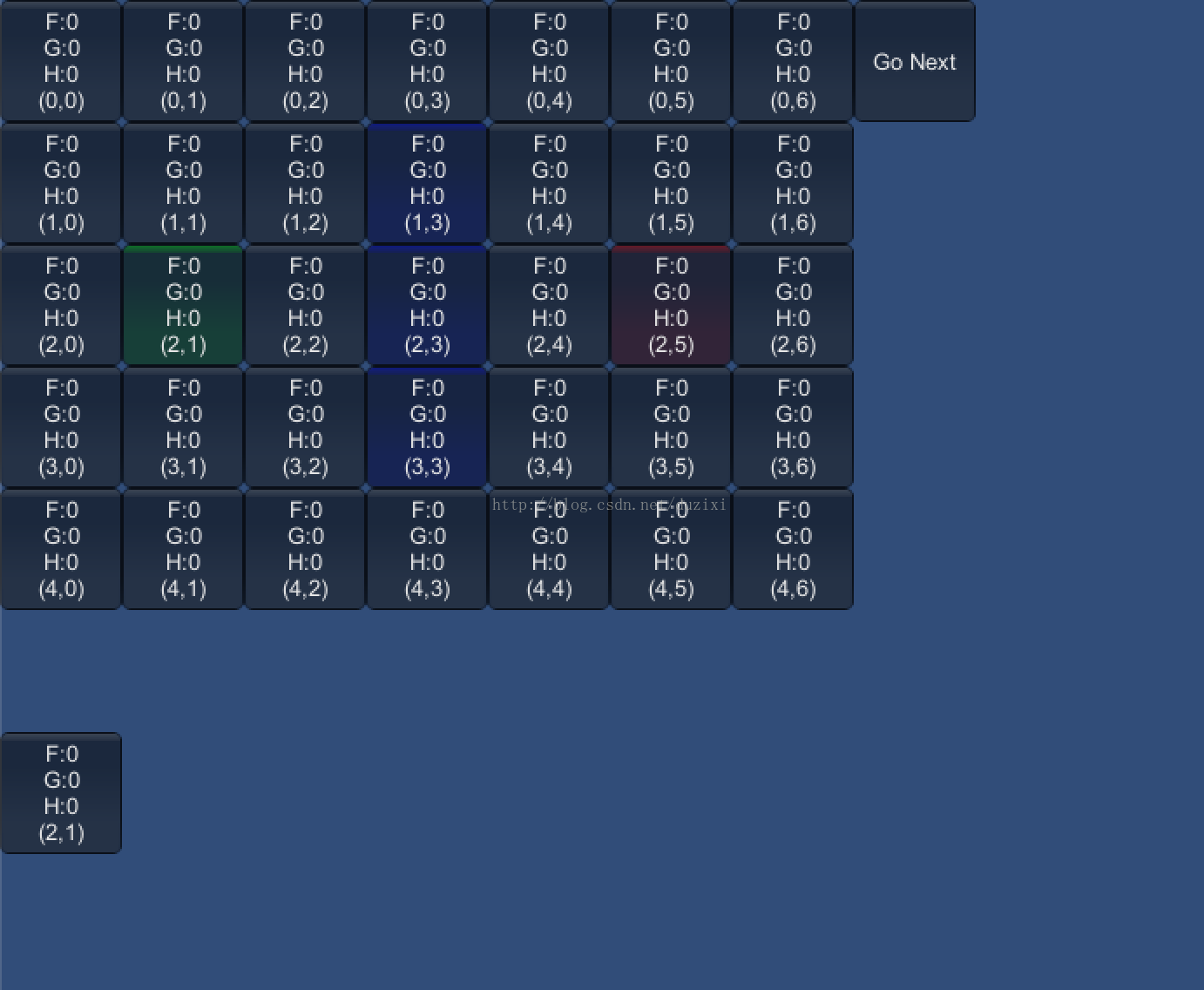
(注:最终找到的路径在控制台里可看到,这个部分没有可视化)
后语
A*算法的具体实现细节有很多,本文脚本只是给出了其中一种。
另外,按照这个算法障碍墙是可以斜穿的,若要避免斜穿还需进一步修改。
