废话不多说,直接上代码吧!
"""
# 利用 diabetes数据集来学习线性回归
# diabetes 是一个关于糖尿病的数据集, 该数据集包括442个病人的生理数据及一年以后的病情发展情况。
# 数据集中的特征值总共10项, 如下:
# 年龄
# 性别
#体质指数
#血压
#s1,s2,s3,s4,s4,s6 (六种血清的化验数据)
#但请注意,以上的数据是经过特殊处理, 10个数据中的每个都做了均值中心化处理,然后又用标准差乘以个体数量调整了数值范围。
#验证就会发现任何一列的所有数值平方和为1.
"""
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import numpy as np
from sklearn import datasets, linear_model
from sklearn.metrics import mean_squared_error, r2_score
# Load the diabetes dataset
diabetes = datasets.load_diabetes()
# Use only one feature
# 增加一个维度,得到一个体质指数数组[[1],[2],...[442]]
diabetes_X = diabetes.data[:, np.newaxis,2]
print(diabetes_X)
# Split the data into training/testing sets
diabetes_X_train = diabetes_X[:-20]
diabetes_X_test = diabetes_X[-20:]
# Split the targets into training/testing sets
diabetes_y_train = diabetes.target[:-20]
diabetes_y_test = diabetes.target[-20:]
# Create linear regression object
regr = linear_model.LinearRegression()
# Train the model using the training sets
regr.fit(diabetes_X_train, diabetes_y_train)
# Make predictions using the testing set
diabetes_y_pred = regr.predict(diabetes_X_test)
# The coefficients
# 查看相关系数
print('Coefficients: \n', regr.coef_)
# The mean squared error
# 均方差
# 查看残差平方的均值(mean square error,MSE)
print("Mean squared error: %.2f"
% mean_squared_error(diabetes_y_test, diabetes_y_pred))
# Explained variance score: 1 is perfect prediction
# R2 决定系数(拟合优度)
# 模型越好:r2→1
# 模型越差:r2→0
print('Variance score: %.2f' % r2_score(diabetes_y_test, diabetes_y_pred))
# Plot outputs
plt.scatter(diabetes_X_test, diabetes_y_test, color='black')
plt.plot(diabetes_X_test, diabetes_y_pred, color='blue', linewidth=3)
plt.xticks(())
plt.yticks(())
plt.show()
对于回归模型效果的判断指标经过了几个过程,从SSE到R-square再到Ajusted R-square, 是一个完善的过程:
SSE(误差平方和):The sum of squares due to error
R-square(决定系数):Coefficient of determination
Adjusted R-square:Degree-of-freedom adjusted coefficient of determination
下面我对以上几个名词进行详细的解释下,相信能给大家带来一定的帮助!!
一、SSE(误差平方和)
计算公式如下:
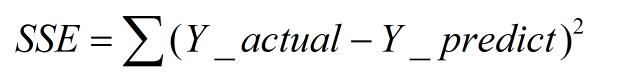
同样的数据集的情况下,SSE越小,误差越小,模型效果越好
缺点:
SSE数值大小本身没有意义,随着样本增加,SSE必然增加,也就是说,不同的数据集的情况下,SSE比较没有意义
二、R-square(决定系数)

数学理解: 分母理解为原始数据的离散程度,分子为预测数据和原始数据的误差,二者相除可以消除原始数据离散程度的影响
其实“决定系数”是通过数据的变化来表征一个拟合的好坏。
理论上取值范围(-∞,1], 正常取值范围为[0 1] ------实际操作中通常会选择拟合较好的曲线计算R²,因此很少出现-∞
越接近1,表明方程的变量对y的解释能力越强,这个模型对数据拟合的也较好
越接近0,表明模型拟合的越差
经验值:>0.4, 拟合效果好
缺点:
数据集的样本越大,R²越大,因此,不同数据集的模型结果比较会有一定的误差
三、Adjusted R-Square (校正决定系数)

n为样本数量,p为特征数量
消除了样本数量和特征数量的影响
以上这篇Python 线性回归分析以及评价指标详解就是小编分享给大家的全部内容了,希望能给大家一个参考,也希望大家多多支持自学编程网。

- 本文固定链接: https://zxbcw.cn/post/183987/
- 转载请注明:必须在正文中标注并保留原文链接
- QQ群: PHP高手阵营官方总群(344148542)
- QQ群: Yii2.0开发(304864863)
