一、校验分类
数据的校验一般分为**前端校验、后端校验**
二、前端校验
前端校验是最为明显的,先说一下:
① HTML
非空校验 如 HTML5 新增的属性required="true",一旦没有填写就输入框就显示红色,具体使用如:
<input type="text" id="name" name="name" required="true"/>
② JS
同时在提交表单发送 Ajax请求 的时候,来个 onSubmit 函数,具体例如(使用点 EasyUI ):
function submitData(){
$("#fm").form("submit",{
url:"/admin/film/save",
onSubmit:function(){
var content=CKEDITOR.instances.content.getData();
if(content==""){
$.messager.alert("系统提示","内容不能为空!");
return false;
}
return $(this).form("validate");
},
success:function(result){
var result=eval('('+result+')');
if(result.success){
$.messager.alert("系统提示","保存成功!");
resetValue();
}else{
$.messager.alert("系统提示","保存失败!");
}
}
});
}
但我们都知道,这是防君子不防小人的做法,用户可以使用 F12,查看源码,修改关键部位的代码,
如把 required="true" 删除掉,就可以提交表单了。
所以前端作用虽然明显,但是数据处理方面,真正用处并不大。
三、后端校验
前面说了那么多,就是为了引出 后端校验 这一话题。数据是否提交到数据库中去,就看后端的代码了。
后端校验,主要实施在 JavaBean、Controller 中。下面列举一个简单的例子,从代码中说明一切。
① 代码结构图
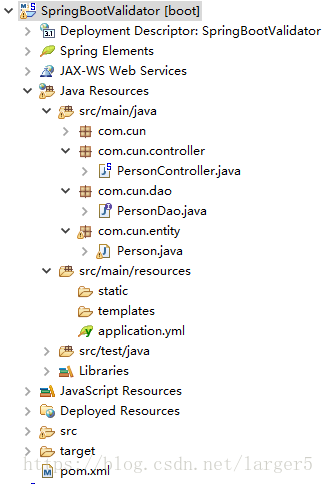
② entity
实体属性部位空,一般使用如 @NotEmpty(message="请输入用户名!") ,这样既不能为 空 ,也不能为null
package com.cun.entity;
import javax.persistence.Column;
import javax.persistence.Entity;
import javax.persistence.GeneratedValue;
import javax.persistence.Id;
import javax.persistence.Table;
import javax.validation.constraints.Max;
import javax.validation.constraints.Min;
import javax.validation.constraints.NotNull;
import javax.validation.constraints.Null;
import javax.validation.constraints.Size;
import org.hibernate.validator.constraints.Email;
import org.hibernate.validator.constraints.NotBlank;
import io.swagger.annotations.ApiModelProperty;
@Entity
@Table(name = "t_person")
public class Person {
@Id
@GeneratedValue
@ApiModelProperty(value = "用户id")
private Integer id;
@NotBlank(message = "用户名不能为空") // 为""/''都不行
@Size(min = 2, max = 30, message = "2<长度<30")
@Column(length = 50)
@ApiModelProperty(value = "用户名")
private String userName;
@NotNull(message = "用户密码不能为空")
@Column(length = 50)
@ApiModelProperty(value = "用户密码")
private String password;
@Max(value = 150, message = "age应<150") // 数字
@Min(value = 1, message = "age应>1") // 数字
@NotNull(message = "年龄不能为空")
@ApiModelProperty(value = "用户年龄")
private Integer age;
@NotNull(message = "邮箱不为空")
@Email(message = "邮件格式不对")
@Column(length = 100)
@ApiModelProperty(value = "用户邮箱")
private String email;
// 使用 JPA 必备
public Person() {
super();
}
public Integer getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(Integer id) {
this.id = id;
}
public String getUserName() {
return userName;
}
public void setUserName(String userName) {
this.userName = userName;
}
public String getPassword() {
return password;
}
public void setPassword(String password) {
this.password = password;
}
public Integer getAge() {
return age;
}
public void setAge(Integer age) {
this.age = age;
}
public String getEmail() {
return email;
}
public void setEmail(String email) {
this.email = email;
}
}
③ dao
其实也没什么代码,这就是 JPA 的强大之处
package com.cun.dao;
import org.springframework.data.jpa.repository.JpaRepository;
import org.springframework.data.jpa.repository.JpaSpecificationExecutor;
import com.cun.entity.Person;
public interface PersonDao extends JpaRepository<Person, Integer>, JpaSpecificationExecutor<Person> {
}
④ Service、ServiceImpl (省略)
⑤ Controller
package com.cun.controller;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Map;
import javax.validation.Valid;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.validation.BindingResult;
import org.springframework.validation.ObjectError;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.PostMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
import com.cun.dao.PersonDao;
import com.cun.entity.Person;
import springfox.documentation.swagger2.annotations.EnableSwagger2;
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/person")
@EnableSwagger2
public class PersonController {
@Autowired
private PersonDao personDao;
@PostMapping("/insert")
public Map<String, Object> insertPerson(@Valid Person person, BindingResult bindingResult) {
Map<String, Object> map = new HashMap<String, Object>();
if (bindingResult.hasErrors()) {
List<ObjectError> errorList = bindingResult.getAllErrors();
List<String> mesList=new ArrayList<String>();
for (int i = 0; i < errorList.size(); i++) {
mesList.add(errorList.get(i).getDefaultMessage());
}
map.put("status", false);
map.put("error", mesList);
} else {
map.put("status", true);
map.put("msg", "添加成功");
personDao.save(person);
}
return map;
}
}
⑥ yml
server: port: 80 #为了以后访问项目不用写端口号 context-path: / #为了以后访问项目不用写项目名 spring: datasource: driver-class-name: com.mysql.jdbc.Driver url: jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/springboot username: root password: 123 jpa: hibernate: ddl-auto: update #数据库同步代码 show-sql: true #dao操作时,显示sql语句
⑦ POM
使用 SpringBoot Starter 导入 JPA、MySQL
使用 Swagger 演示
<!-- swagger生成接口API --> <dependency> <groupId>io.springfox</groupId> <artifactId>springfox-swagger2</artifactId> <version>2.7.0</version> </dependency> <!-- 接口API生成html文档 --> <dependency> <groupId>io.springfox</groupId> <artifactId>springfox-swagger-ui</artifactId> <version>2.6.1</version> </dependency>
四、演示
输入 http://localhost/swagger-ui.html 进入接口测试站点
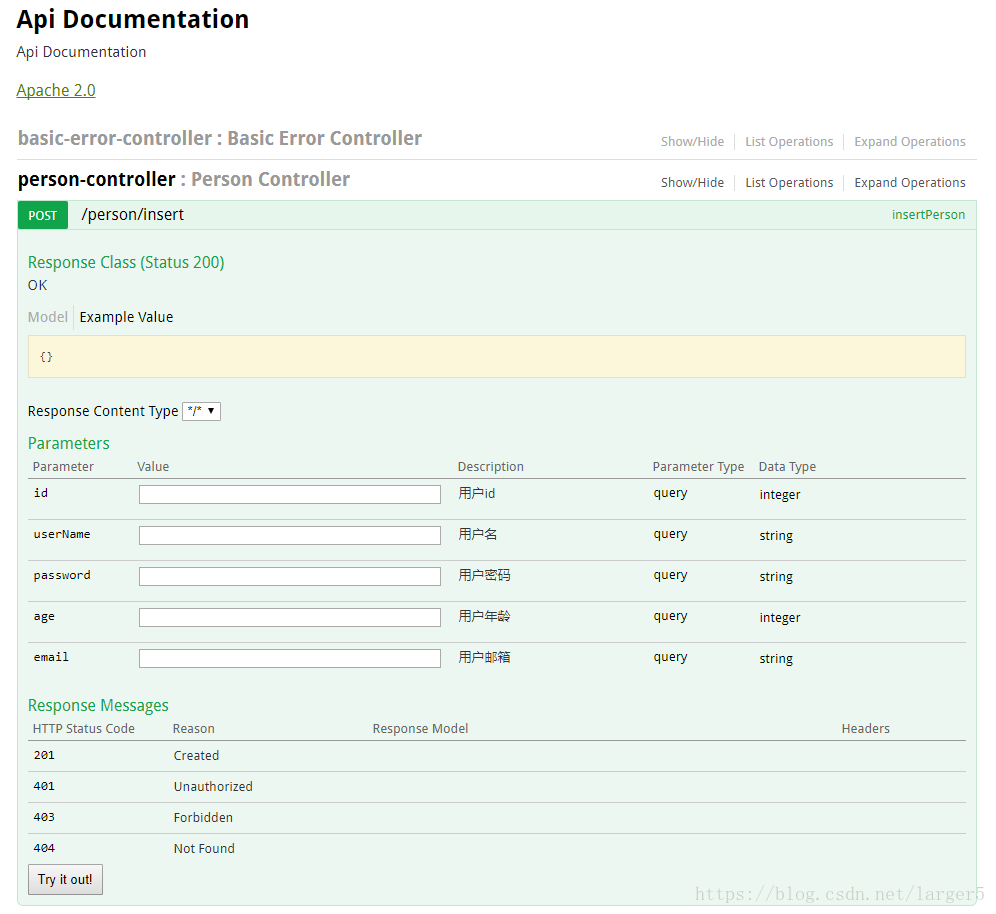
什么都没有填写,直接点击Try it out!,可以看到返回给前端的 JSON 数据,这时候数据的数据是没有改动的,一条sql 语句都没有执行

当然还可以进行其他测试,这里就省略了
到此这篇关于SpringBoot结合JSR303对前端数据进行校验的示例代码的文章就介绍到这了,更多相关SpringBoot JSR303校验内容请搜索自学编程网以前的文章或继续浏览下面的相关文章希望大家以后多多支持自学编程网!

- 本文固定链接: https://zxbcw.cn/post/194730/
- 转载请注明:必须在正文中标注并保留原文链接
- QQ群: PHP高手阵营官方总群(344148542)
- QQ群: Yii2.0开发(304864863)
