一、Selector设计
笔者下载得是openjdk8的源码, 画出类图
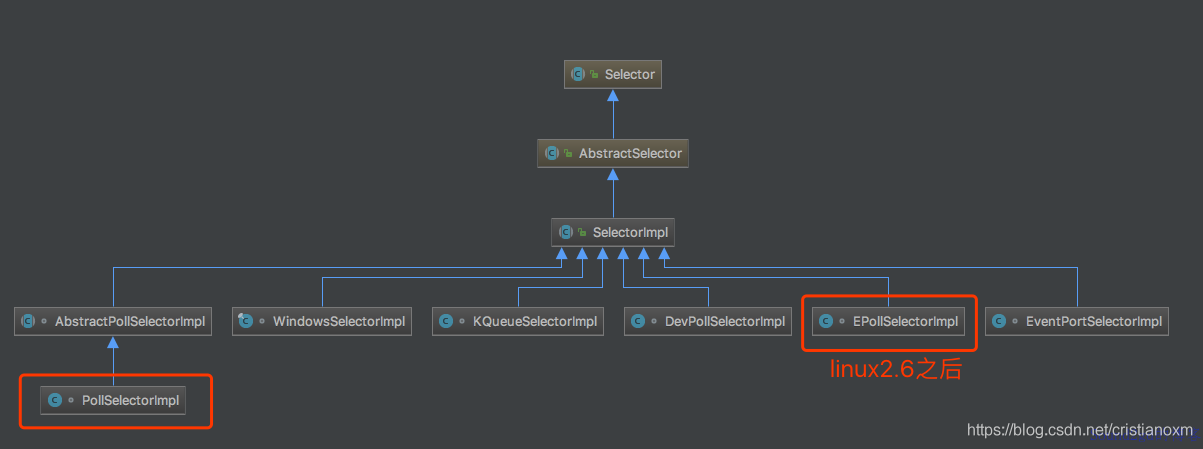
比较清晰得看到,openjdk中Selector的实现是SelectorImpl,然后SelectorImpl又将职责委托给了具体的平台,比如图中框出的
- linux2.6以后才有的
EpollSelectorImpl - Windows平台是
WindowsSelectorImpl - MacOSX平台是
KQueueSelectorImpl
从名字也可以猜到,openjdk肯定在底层还是用epoll,kqueue,iocp这些技术来实现的I/O多路复用。
二、获取Selector
众所周知,Selector.open()可以得到一个Selector实例,怎么实现的呢?
// Selector.java
public static Selector open() throws IOException {
// 首先找到provider,然后再打开Selector
return SelectorProvider.provider().openSelector();
}
// java.nio.channels.spi.SelectorProvider
public static SelectorProvider provider() {
synchronized (lock) {
if (provider != null)
return provider;
return AccessController.doPrivileged(
new PrivilegedAction<SelectorProvider>() {
public SelectorProvider run() {
if (loadProviderFromProperty())
return provider;
if (loadProviderAsService())
return provider;
// 这里就是打开Selector的真正方法
provider = sun.nio.ch.DefaultSelectorProvider.create();
return provider;
}
});
}
}
在openjdk中,每个操作系统都有一个sun.nio.ch.DefaultSelectorProvider实现,以solaris为例:
/**
* Returns the default SelectorProvider.
*/
public static SelectorProvider create() {
// 获取OS名称
String osname = AccessController
.doPrivileged(new GetPropertyAction("os.name"));
// 根据名称来创建不同的Selctor
if (osname.equals("SunOS"))
return createProvider("sun.nio.ch.DevPollSelectorProvider");
if (osname.equals("Linux"))
return createProvider("sun.nio.ch.EPollSelectorProvider");
return new sun.nio.ch.PollSelectorProvider();
}
如果系统名称是Linux的话,真正创建的是sun.nio.ch.EPollSelectorProvider。如果不是SunOS也不是Linux,就使用sun.nio.ch.PollSelectorProvider, 关于PollSelector有兴趣的读者自行了解下, 本文仅以实际常用的EpollSelector为例探讨。
打开sun.nio.ch.EPollSelectorProvider查看openSelector方法
public AbstractSelector openSelector() throws IOException {
return new EPollSelectorImpl(this);
}
很直观,这样我们在Linux平台就得到了最终的Selector实现:sun.nio.ch.EPollSelectorImpl
三、EPollSelector如何进行select
epoll系统调用主要分为3个函数
epoll_create: 创建一个epollfd,并开辟epoll自己的内核高速cache区,建立红黑树,分配好想要的size的内存对象,建立一个list链表,用于存储准备就绪的事件。epoll_wait: 等待内核返回IO事件epoll_ctl: 对新旧事件进行新增修改或者删除
3.1 Epoll fd的创建
EPollSelectorImpl的构造器代码如下:
EPollSelectorImpl(SelectorProvider sp) throws IOException {
super(sp);
// makePipe返回管道的2个文件描述符,编码在一个long类型的变量中
// 高32位代表读 低32位代表写
// 使用pipe为了实现Selector的wakeup逻辑
long pipeFds = IOUtil.makePipe(false);
fd0 = (int) (pipeFds >>> 32);
fd1 = (int) pipeFds;
// 新建一个EPollArrayWrapper
pollWrapper = new EPollArrayWrapper();
pollWrapper.initInterrupt(fd0, fd1);
fdToKey = new HashMap<>();
}
再看EPollArrayWrapper的初始化过程
EPollArrayWrapper() throws IOException {
// creates the epoll file descriptor
// 创建epoll fd
epfd = epollCreate();
// the epoll_event array passed to epoll_wait
int allocationSize = NUM_EPOLLEVENTS * SIZE_EPOLLEVENT;
pollArray = new AllocatedNativeObject(allocationSize, true);
pollArrayAddress = pollArray.address();
// eventHigh needed when using file descriptors > 64k
if (OPEN_MAX > MAX_UPDATE_ARRAY_SIZE)
eventsHigh = new HashMap<>();
}
private native int epollCreate();
在初始化过程中调用了epollCreate方法,这是个native方法。
打开
jdk/src/solaris/native/sun/nio/ch/EPollArrayWrapper.c
EPollArrayWrapper() throws IOException {
// creates the epoll file descriptor
// 创建epoll fd
epfd = epollCreate();
// the epoll_event array passed to epoll_wait
int allocationSize = NUM_EPOLLEVENTS * SIZE_EPOLLEVENT;
pollArray = new AllocatedNativeObject(allocationSize, true);
pollArrayAddress = pollArray.address();
// eventHigh needed when using file descriptors > 64k
if (OPEN_MAX > MAX_UPDATE_ARRAY_SIZE)
eventsHigh = new HashMap<>();
}
private native int epollCreate();
可以看到最后还是使用了操作系统的api: epoll_create函数
3.2 Epoll wait等待内核IO事件
调用Selector.select(),最后会委托给各个实现的doSelect方法,限于篇幅不贴出太详细的,这里看下EpollSelectorImpl的doSelect方法
protected int doSelect(long timeout) throws IOException {
if (closed)
throw new ClosedSelectorException();
processDeregisterQueue();
try {
begin();
// 真正的实现是这行
pollWrapper.poll(timeout);
} finally {
end();
}
processDeregisterQueue();
int numKeysUpdated = updateSelectedKeys();
// 以下基本都是异常处理
if (pollWrapper.interrupted()) {
// Clear the wakeup pipe
pollWrapper.putEventOps(pollWrapper.interruptedIndex(), 0);
synchronized (interruptLock) {
pollWrapper.clearInterrupted();
IOUtil.drain(fd0);
interruptTriggered = false;
}
}
return numKeysUpdated;
}
然后我们去看pollWrapper.poll, 打开jdk/src/solaris/classes/sun/nio/ch/EPollArrayWrapper.java:
int poll(long timeout) throws IOException {
updateRegistrations();
// 这个epollWait是不是有点熟悉呢?
updated = epollWait(pollArrayAddress, NUM_EPOLLEVENTS, timeout, epfd);
for (int i=0; i<updated; i++) {
if (getDescriptor(i) == incomingInterruptFD) {
interruptedIndex = i;
interrupted = true;
break;
}
}
return updated;
}
private native int epollWait(long pollAddress, int numfds, long timeout,
int epfd) throws IOException;
epollWait也是个native方法,打开c代码一看:
JNIEXPORT jint JNICALL
Java_sun_nio_ch_EPollArrayWrapper_epollWait(JNIEnv *env, jobject this,
jlong address, jint numfds,
jlong timeout, jint epfd)
{
struct epoll_event *events = jlong_to_ptr(address);
int res;
if (timeout <= 0) { /* Indefinite or no wait */
// 发起epoll_wait系统调用等待内核事件
RESTARTABLE(epoll_wait(epfd, events, numfds, timeout), res);
} else { /* Bounded wait; bounded restarts */
res = iepoll(epfd, events, numfds, timeout);
}
if (res < 0) {
JNU_ThrowIOExceptionWithLastError(env, "epoll_wait failed");
}
return res;
}
=
可以看到,最后还是发起的epoll_wait系统调用.
3.3 epoll control以及openjdk对事件管理的封装
JDK中对于注册到Selector上的IO事件关系是使用SelectionKey来表示,代表了Channel感兴趣的事件,如Read,Write,Connect,Accept.
调用Selector.register()时均会将事件存储到EpollArrayWrapper的成员变量eventsLow和eventsHigh中
// events for file descriptors with registration changes pending, indexed
// by file descriptor and stored as bytes for efficiency reasons. For
// file descriptors higher than MAX_UPDATE_ARRAY_SIZE (unlimited case at
// least) then the update is stored in a map.
// 使用数组保存事件变更, 数组的最大长度是MAX_UPDATE_ARRAY_SIZE, 最大64*1024
private final byte[] eventsLow = new byte[MAX_UPDATE_ARRAY_SIZE];
// 超过数组长度的事件会缓存到这个map中,等待下次处理
private Map<Integer,Byte> eventsHigh;
/**
* Sets the pending update events for the given file descriptor. This
* method has no effect if the update events is already set to KILLED,
* unless {@code force} is {@code true}.
*/
private void setUpdateEvents(int fd, byte events, boolean force) {
// 判断fd和数组长度
if (fd < MAX_UPDATE_ARRAY_SIZE) {
if ((eventsLow[fd] != KILLED) || force) {
eventsLow[fd] = events;
}
} else {
Integer key = Integer.valueOf(fd);
if (!isEventsHighKilled(key) || force) {
eventsHigh.put(key, Byte.valueOf(events));
}
}
}
上面看到EpollArrayWrapper.poll()的时候, 首先会调用updateRegistrations
/**
* Returns the pending update events for the given file descriptor.
*/
private byte getUpdateEvents(int fd) {
if (fd < MAX_UPDATE_ARRAY_SIZE) {
return eventsLow[fd];
} else {
Byte result = eventsHigh.get(Integer.valueOf(fd));
// result should never be null
return result.byteValue();
}
}
/**
* Update the pending registrations.
*/
private void updateRegistrations() {
synchronized (updateLock) {
int j = 0;
while (j < updateCount) {
int fd = updateDescriptors[j];
// 从保存的eventsLow和eventsHigh里取出事件
short events = getUpdateEvents(fd);
boolean isRegistered = registered.get(fd);
int opcode = 0;
if (events != KILLED) {
// 判断操作类型以传给epoll_ctl
// 没有指定EPOLLET事件类型
if (isRegistered) {
opcode = (events != 0) ? EPOLL_CTL_MOD : EPOLL_CTL_DEL;
} else {
opcode = (events != 0) ? EPOLL_CTL_ADD : 0;
}
if (opcode != 0) {
// 熟悉的epoll_ctl
epollCtl(epfd, opcode, fd, events);
if (opcode == EPOLL_CTL_ADD) {
registered.set(fd);
} else if (opcode == EPOLL_CTL_DEL) {
registered.clear(fd);
}
}
}
j++;
}
updateCount = 0;
}
}
private native void epollCtl(int epfd, int opcode, int fd, int events);
在获取到事件之后将操作委托给了epollCtl,这又是个native方法,打开相应的c代码一看:
JNIEXPORT void JNICALL
Java_sun_nio_ch_EPollArrayWrapper_epollCtl(JNIEnv *env, jobject this, jint epfd,
jint opcode, jint fd, jint events)
{
struct epoll_event event;
int res;
event.events = events;
event.data.fd = fd;
// 发起epoll_ctl调用来进行IO事件的管理
RESTARTABLE(epoll_ctl(epfd, (int)opcode, (int)fd, &event), res);
/*
* A channel may be registered with several Selectors. When each Selector
* is polled a EPOLL_CTL_DEL op will be inserted into its pending update
* list to remove the file descriptor from epoll. The "last" Selector will
* close the file descriptor which automatically unregisters it from each
* epoll descriptor. To avoid costly synchronization between Selectors we
* allow pending updates to be processed, ignoring errors. The errors are
* harmless as the last update for the file descriptor is guaranteed to
* be EPOLL_CTL_DEL.
*/
if (res < 0 && errno != EBADF && errno != ENOENT && errno != EPERM) {
JNU_ThrowIOExceptionWithLastError(env, "epoll_ctl failed");
}
}
原来还是我们的老朋友epoll_ctl.
有个小细节是jdk没有指定ET(边缘触发)还是LT(水平触发),所以默认会用LT:)
在AbstractSelectorImpl中有3个set保存事件
// Public views of the key sets // 注册的所有事件 private Set<SelectionKey> publicKeys; // Immutable // 内核返回的IO事件封装,表示哪些fd有数据可读可写 private Set<SelectionKey> publicSelectedKeys; // Removal allowed, but not addition // 取消的事件 private final Set<SelectionKey> cancelledKeys = new HashSet<SelectionKey>();
在EpollArrayWrapper.poll调用完成之后, 会调用updateSelectedKeys来更新上面的仨set
private int updateSelectedKeys() {
int entries = pollWrapper.updated;
int numKeysUpdated = 0;
for (int i=0; i<entries; i++) {
int nextFD = pollWrapper.getDescriptor(i);
SelectionKeyImpl ski = fdToKey.get(Integer.valueOf(nextFD));
// ski is null in the case of an interrupt
if (ski != null) {
int rOps = pollWrapper.getEventOps(i);
if (selectedKeys.contains(ski)) {
if (ski.channel.translateAndSetReadyOps(rOps, ski)) {
numKeysUpdated++;
}
} else {
ski.channel.translateAndSetReadyOps(rOps, ski);
if ((ski.nioReadyOps() & ski.nioInterestOps()) != 0) {
selectedKeys.add(ski);
numKeysUpdated++;
}
}
}
}
return numKeysUpdated;
代码很直白,拿出事件对set比对操作。
四、Selector类的相关方法

重点注意四个方法
- select():
这是一个阻塞方法,调用该方法,会阻塞,直到返回一个有事件发生的selectionKey集合 - selectNow() :非阻塞方法,
获取不到有事件发生的selectionKey集合,也会立即返回 - select(long):阻塞方法,
如果没有获取到有事件发生的selectionKey集合,阻塞指定的long时间 - selectedKeys(): 返回全部selectionKey集合,不管是否有事件发生

可以理解:selector一直在监听select()
五、Selector、SelectionKey、ServerScoketChannel、ScoketChannel的关系
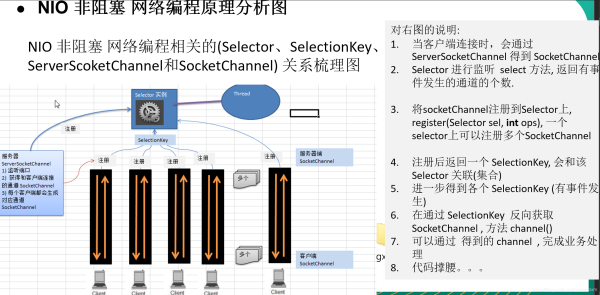
Server代码:
public class NIOServer {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception{
//创建ServerSocketChannel -> ServerSocket
ServerSocketChannel serverSocketChannel = ServerSocketChannel.open();
//得到一个Selecor对象
Selector selector = Selector.open();
//绑定一个端口6666, 在服务器端监听
serverSocketChannel.socket().bind(new InetSocketAddress(6666));
//设置为非阻塞
serverSocketChannel.configureBlocking(false);
//把 serverSocketChannel 注册到 selector 关心 事件为 OP_ACCEPT
serverSocketChannel.register(selector, SelectionKey.OP_ACCEPT);
System.out.println("注册后的selectionkey 数量=" + selector.keys().size()); // 1
//循环等待客户端连接
while (true) {
//这里我们等待1秒,如果没有事件发生, 返回
if(selector.select(1000) == 0) { //没有事件发生
System.out.println("服务器等待了1秒,无连接");
continue;
}
//如果返回的>0, 就获取到相关的 selectionKey集合
//1.如果返回的>0, 表示已经获取到关注的事件
//2. selector.selectedKeys() 返回关注事件的集合
// 通过 selectionKeys 反向获取通道
Set<SelectionKey> selectionKeys = selector.selectedKeys();
System.out.println("selectionKeys 数量 = " + selectionKeys.size());
//遍历 Set<SelectionKey>, 使用迭代器遍历
Iterator<SelectionKey> keyIterator = selectionKeys.iterator();
while (keyIterator.hasNext()) {
//获取到SelectionKey
SelectionKey key = keyIterator.next();
//根据key 对应的通道发生的事件做相应处理
if(key.isAcceptable()) { //如果是 OP_ACCEPT, 有新的客户端连接
//该该客户端生成一个 SocketChannel
SocketChannel socketChannel = serverSocketChannel.accept();
System.out.println("客户端连接成功 生成了一个 socketChannel " + socketChannel.hashCode());
//将 SocketChannel 设置为非阻塞
socketChannel.configureBlocking(false);
//将socketChannel 注册到selector, 关注事件为 OP_READ, 同时给socketChannel
//关联一个Buffer
socketChannel.register(selector, SelectionKey.OP_READ, ByteBuffer.allocate(1024));
System.out.println("客户端连接后 ,注册的selectionkey 数量=" + selector.keys().size()); //2,3,4..
}
if(key.isReadable()) { //发生 OP_READ
//通过key 反向获取到对应channel
SocketChannel channel = (SocketChannel)key.channel();
//获取到该channel关联的buffer
ByteBuffer buffer = (ByteBuffer)key.attachment();
channel.read(buffer);
System.out.println("form 客户端 " + new String(buffer.array()));
}
//手动从集合中移动当前的selectionKey, 防止重复操作
keyIterator.remove();
}
}
}
}
Client代码
public class NIOClient {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception{
//得到一个网络通道
SocketChannel socketChannel = SocketChannel.open();
//设置非阻塞
socketChannel.configureBlocking(false);
//提供服务器端的ip 和 端口
InetSocketAddress inetSocketAddress = new InetSocketAddress("127.0.0.1", 6666);
//连接服务器
if (!socketChannel.connect(inetSocketAddress)) {
while (!socketChannel.finishConnect()) {
System.out.println("因为连接需要时间,客户端不会阻塞,可以做其它工作..");
}
}
//...如果连接成功,就发送数据
String str = "hello, 尚硅谷~";
//Wraps a byte array into a buffer
ByteBuffer buffer = ByteBuffer.wrap(str.getBytes());
//发送数据,将 buffer 数据写入 channel
socketChannel.write(buffer);
System.in.read();
}
}
六、总结

jdk中Selector是对操作系统的IO多路复用调用的一个封装,在Linux中就是对epoll的封装。epoll实质上是将event loop交给了内核,因为网络数据都是首先到内核的,直接内核处理可以避免无谓的系统调用和数据拷贝, 性能是最好的。jdk中对IO事件的封装是SelectionKey, 保存Channel关心的事件。
到此这篇关于Java进阶之高并发核心Selector详解的文章就介绍到这了,更多相关高并发核心Selector内容请搜索自学编程网以前的文章或继续浏览下面的相关文章希望大家以后多多支持自学编程网!

- 本文固定链接: https://zxbcw.cn/post/212119/
- 转载请注明:必须在正文中标注并保留原文链接
- QQ群: PHP高手阵营官方总群(344148542)
- QQ群: Yii2.0开发(304864863)
