一、前言
序列化:将对象转换为二进制序列在网络中传输或保存到磁盘
反序列化:从网络或磁盘中将二进制序列转换为对象
注意:
- 对象必须实现Serializable接口
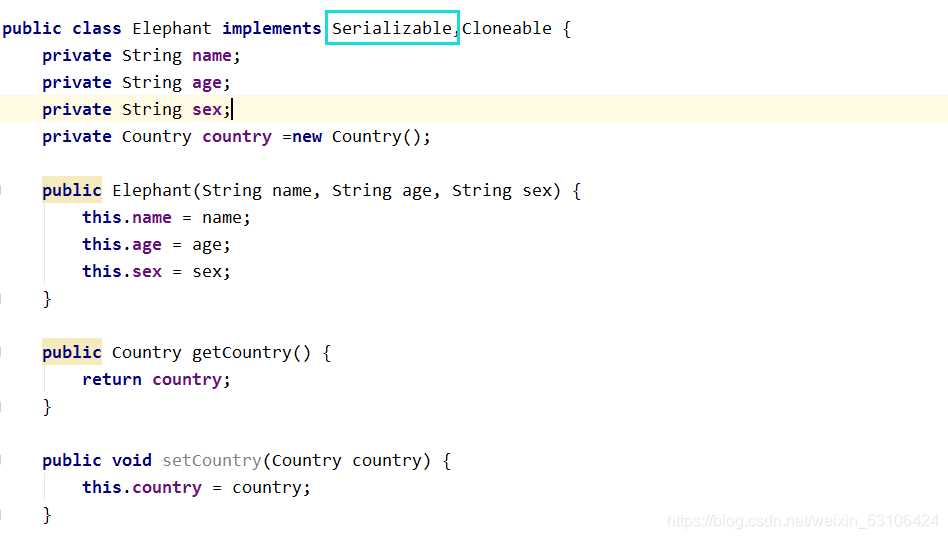
- 对象的所有属性都要能序列化(Integer,Byte等都进行了序列化)
1.1 String
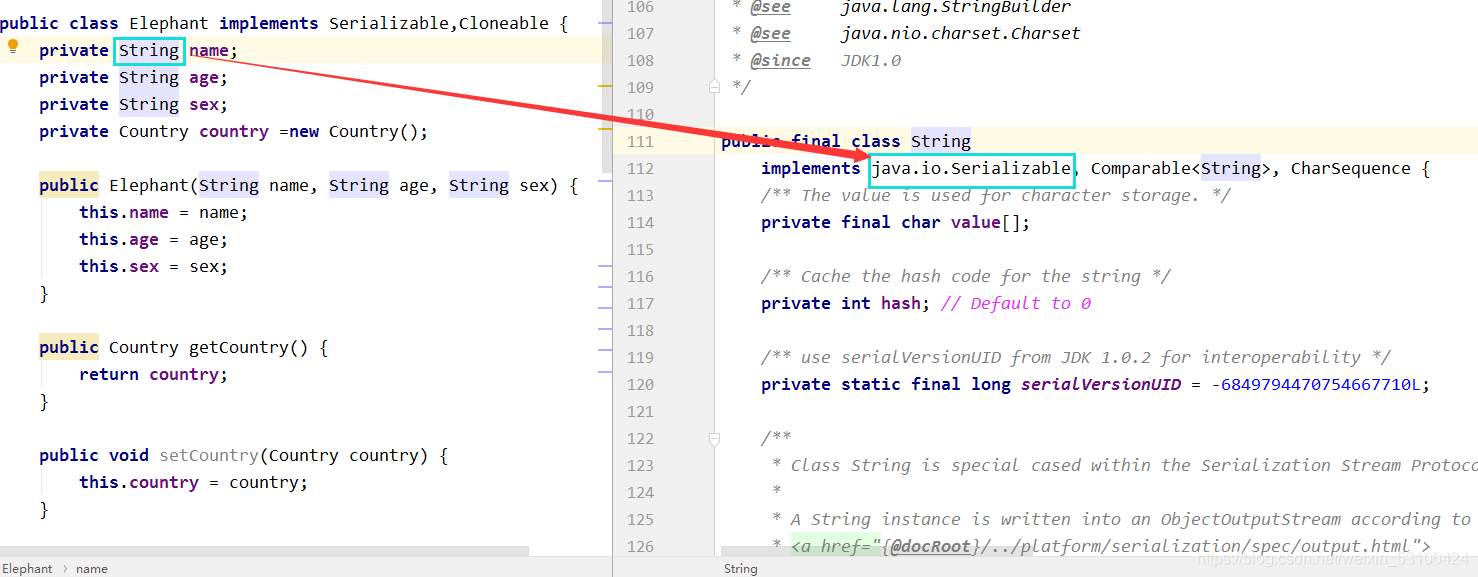
1.2 Integer
二、案例
2.1 编写大象类
public class Elephant implements Serializable {
private String name;
private String age;
private String sex;
public Elephant(String name, String age, String sex) {
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
this.sex = sex;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Elephant{" +
"name='" + name + '\'' +
", age='" + age + '\'' +
", sex='" + sex + '\'' +
'}';
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public String getAge() {
return age;
}
public void setAge(String age) {
this.age = age;
}
public String getSex() {
return sex;
}
public void setSex(String sex) {
this.sex = sex;
}
}
2.2 大象测试类
public class ElephantTest {
public static final String PATH = "D:\\elephant";
static void write(Elephant elephant){
//创建对象输出流
try( ObjectOutputStream out = new ObjectOutputStream(new FileOutputStream(PATH))) {
//写入对象
out.writeObject(elephant);
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
static Object read(){
//创建对象输出流
try( ObjectInputStream in = new ObjectInputStream(new FileInputStream(PATH))) {
//写入对象
return in.readObject();
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
return null;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Elephant elephant7 = new Elephant("小红象", "18", "男");
write(elephant7);
Elephant elephant1 = (Elephant) read();
System.out.println(elephant1);
System.out.println(elephant7);
System.out.println(elephant1==elephant7);
}
}
三、运行结果
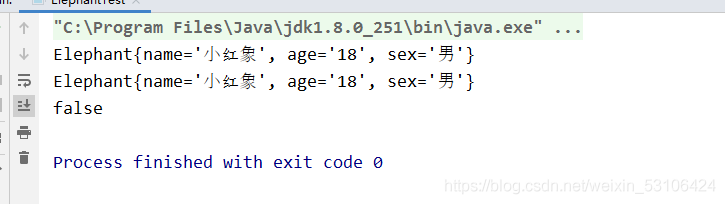
写入D盘的对象:
到此这篇关于深入理解Java序列化与反序列化的文章就介绍到这了,更多相关Java序列化与反序列化内容请搜索自学编程网以前的文章或继续浏览下面的相关文章希望大家以后多多支持自学编程网!

- 本文固定链接: https://zxbcw.cn/post/212410/
- 转载请注明:必须在正文中标注并保留原文链接
- QQ群: PHP高手阵营官方总群(344148542)
- QQ群: Yii2.0开发(304864863)
