Gateway请求转发
本期我们主要还是讲解一下Gateway,上一期我们讲解了一下Gateway中进行路由转发的关键角色,过滤器和断言是如何被加载的,上期链接://www.jb51.net/article/211824.htm
好了我们废话不多说,开始今天的Gateway请求转发流程讲解,为了在讲解源码的时候,以防止大家可能会迷糊,博主专门画了一下源码流程图,链接地址://www.jb51.net/article/211824.htm
上一期我们已经知道了相关类的加载,今天直接从源码开始,大家可能不太了解webflux和reactor这种响应式编程,毕竟不是主流,我们一直用的都是spring MVC,没事,我们主要讲解流程,不做过多的讲解。
大家先看下面的代码,我们今天主要的代码入口就是这里:
public Mono<Void> handle(ServerWebExchange exchange) {
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
ServerHttpRequest request = exchange.getRequest();
logger.debug("Processing " + request.getMethodValue() + " request for [" + request.getURI() + "]");
}
if (this.handlerMappings == null) {
return Mono.error(HANDLER_NOT_FOUND_EXCEPTION);
}
return Flux.fromIterable(this.handlerMappings)
.concatMap(mapping -> mapping.getHandler(exchange))
.next()
.switchIfEmpty(Mono.error(HANDLER_NOT_FOUND_EXCEPTION))
.flatMap(handler -> invokeHandler(exchange, handler))
.flatMap(result -> handleResult(exchange, result));
}
第一步,我们先来看一看几个主要的类及其方法,Flux 表示的是包含 0 到 N 个元素的异步序列,Mono 表示的是包含 0 或者 1 个元素的异步序列,记住Flux是多个元素集合,Mono 是单个元素集合就很好理解以后的源码了,以下方法注释是博主为了大家好理解而写的,具体实际的意义还是需要大家自行Google学习了。
Mono.empty();创建一个空Mono对象;
Mono.just(**);创建一个**元素的对象;
Mono.then(**);在最后执行,相当于spring的aop后置通知一样
开始我们的第一步解析:mapping.getHandler(exchange);本方法主要做的是获取路由,我们继续看一看底层源码:
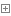
getHandler
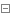
getHandlerInternal
//这里返回的是单个对象
protected Mono<Route> lookupRoute(ServerWebExchange exchange) {
return this.routeLocator
//我们一会主要看一下这个方法
.getRoutes()
//individually filter routes so that filterWhen error delaying is not a problem
.concatMap(route -> Mono
.just(route)
.filterWhen(r -> {
// add the current route we are testing
exchange.getAttributes().put(GATEWAY_PREDICATE_ROUTE_ATTR, r.getId());
//只返回一个符合断言的路由配置,所以整个流程先匹配断言
return r.getPredicate().apply(exchange);
})
//instead of immediately stopping main flux due to error, log and swallow it
.doOnError(e -> logger.error("Error applying predicate for route: "+route.getId(), e))
.onErrorResume(e -> Mono.empty())
)
// .defaultIfEmpty() put a static Route not found
// or .switchIfEmpty()
// .switchIfEmpty(Mono.<Route>empty().log("noroute"))
.next()
//TODO: error handling
.map(route -> {
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Route matched: " + route.getId());
}
validateRoute(route, exchange);
return route;
});
}
我们现在看看Route对象是怎么在getRoutes()创建的。
public Flux<Route> getRoutes() {
return this.routeDefinitionLocator.getRouteDefinitions() //这一步是从配置文件中读取我们配置的路由定义
.map(this::convertToRoute)//这一步会加载我们配置给路由的断言与过滤器形成路由对象
//TODO: error handling
.map(route -> {
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("RouteDefinition matched: " + route.getId());
}
return route;
});
}
//关键的代码在这里
private Route convertToRoute(RouteDefinition routeDefinition) {
//这两步才会跟上一章节讲解的如何加载断言与过滤器有关联,大家可以自行查看底层源码是如何查出来的对象的
AsyncPredicate<ServerWebExchange> predicate = combinePredicates(routeDefinition);
List<GatewayFilter> gatewayFilters = getFilters(routeDefinition);
//终于生成了路由对象
return Route.async(routeDefinition)
.asyncPredicate(predicate)
.replaceFilters(gatewayFilters)
.build();
}
这里大家要记住getHandlerInternal方法,生成了Mono.just(webHandler),仔细看webHandler是FilteringWebHandler对象,以后用到这个WebHandler,好了路由生成也选择完毕了,我们应该知道改请求是否符合我们配置的过滤器了,因为过滤器还没用上,断言只负责了选择哪一个路由生效。
//我们看下一个主流程的方法
private Mono<HandlerResult> invokeHandler(ServerWebExchange exchange, Object handler) {
if (this.handlerAdapters != null) {
for (HandlerAdapter handlerAdapter : this.handlerAdapters) {
if (handlerAdapter.supports(handler)) {
//这里走的是SimpleHandlerAdapter,可以自己debug发现,也可以去找自动配置类找,这里就不讲解了
return handlerAdapter.handle(exchange, handler);
}
}
}
return Mono.error(new IllegalStateException("No HandlerAdapter: " + handler));
}
public Mono<HandlerResult> handle(ServerWebExchange exchange, Object handler) {
WebHandler webHandler = (WebHandler) handler;
//让大家记住的那个FilteringWebHandler类,终于在这里起作用了。我们这回可以看看过滤器是如何起作用的
Mono<Void> mono = webHandler.handle(exchange);
return mono.then(Mono.empty());//过滤器处理完后,开始处理mono.then方法
}
public Mono<Void> handle(ServerWebExchange exchange) {
Route route = exchange.getRequiredAttribute(GATEWAY_ROUTE_ATTR);
List<GatewayFilter> gatewayFilters = route.getFilters();//我们路由自己配置的过滤器
//加载全局过滤器
List<GatewayFilter> combined = new ArrayList<>(this.globalFilters);
combined.addAll(gatewayFilters);
//TODO: needed or cached?
AnnotationAwareOrderComparator.sort(combined);
//排序
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Sorted gatewayFilterFactories: "+ combined);
}
//形成过滤器链,开始调用filter进行过滤。这里剩下的我们就不讲解,跟spring配置的过滤器链调用流程是一样的
return new DefaultGatewayFilterChain(combined).filter(exchange);
}
至此,我们的请求流程基本完事了,我们再来看看几个主要的全局过滤器配置。LoadBalancerClientFilter:负责获取服务器ip的过滤器,NettyRoutingFilter:负责转发我们请求的过滤器。
这里主要讲解Gateway流程,关于Ribbon的代码我们就不做主要讲解了
public Mono<Void> filter(ServerWebExchange exchange, GatewayFilterChain chain) {
URI url = exchange.getAttribute(GATEWAY_REQUEST_URL_ATTR);
String schemePrefix = exchange.getAttribute(GATEWAY_SCHEME_PREFIX_ATTR);
//所以要加上lb前缀,才会走该过滤器
if (url == null || (!"lb".equals(url.getScheme()) && !"lb".equals(schemePrefix))) {
return chain.filter(exchange);
}
//preserve the original url
addOriginalRequestUrl(exchange, url);
log.trace("LoadBalancerClientFilter url before: " + url);
//选择实例
final ServiceInstance instance = choose(exchange);
......
return chain.filter(exchange);
}
看主要代码即可,非必要的看了也晕。
public Mono<Void> filter(ServerWebExchange exchange, GatewayFilterChain chain) {
.......
//通过httpClient发送请求获取响应
Mono<HttpClientResponse> responseMono = this.httpClient.request(method, url, req -> {
final HttpClientRequest proxyRequest = req.options(NettyPipeline.SendOptions::flushOnEach)
.headers(httpHeaders)
.chunkedTransfer(chunkedTransfer)
.failOnServerError(false)
.failOnClientError(false);
if (preserveHost) {
String host = request.getHeaders().getFirst(HttpHeaders.HOST);
proxyRequest.header(HttpHeaders.HOST, host);
}
if (properties.getResponseTimeout() != null) {
proxyRequest.context(ctx -> ctx.addHandlerFirst(
new ReadTimeoutHandler(properties.getResponseTimeout().toMillis(), TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS)));
}
return proxyRequest.sendHeaders() //I shouldn't need this
.send(request.getBody().map(dataBuffer ->
((NettyDataBuffer) dataBuffer).getNativeBuffer()));
});
return responseMono.doOnNext(res -> {
...
}
}
我们今天主要看的是Gateway的主要请求转发的流程,像webflux这种我们没有精力学习的,可以暂时略过,毕竟也不是主流。我们今天最后总结一下。首先在Gateway这两章的点,项目启动时加载断言与过滤器->接收请求时添加配置文件中的路由配置并生成路由对象->找到符合断言的路由->除了个人配置的过滤器联合全局过滤器生成过滤器链,并逐步过滤知道所有调用完成。
其中我们主要分析了两个主要的全局过滤器:LoadBalancerClientFilter:负责获取服务器ip的过滤器,NettyRoutingFilter:负责转发我们请求的过滤器。
到此这篇关于Java源码解析之Gateway请求转发的文章就介绍到这了,更多相关Gateway请求转发内容请搜索自学编程网以前的文章或继续浏览下面的相关文章希望大家以后多多支持自学编程网!

- 本文固定链接: https://zxbcw.cn/post/215842/
- 转载请注明:必须在正文中标注并保留原文链接
- QQ群: PHP高手阵营官方总群(344148542)
- QQ群: Yii2.0开发(304864863)
