使用AOP的原因(AOP简介)
我们知道,spring两大核心,IOC(控制反转)和AOP(切面),那为什么要使用AOP,AOP是什么呢,严格来说,AOP是一种编程规范,是一种编程思想,并非spring创造,AOP可以帮助我们在一定程度上从冗余的通用的业务逻辑中解脱出来,最明显的,比如每个接口的请求,都要记录日志,那这个操作如果每个地方都写,就会很繁琐,当然,记录日志并不是唯一的用法
spring的AOP只能基于IOC来管理,它只能作用于spring容器的bean
并且,spring的AOP为的是解决企业开发中出现最普遍的方法织入,并不是为了像AspectJ那样,成为一个完全的AOP使用解决方案
AOP的使用
开启AOP支持
要使用AOP,首先要开启AOP的支持
<dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-aop</artifactId> </dependency>
启动类添加 @EnableAspectJAutoProxy 注解
编写切面类与测试方法
@Aspect
@Component
public class MyAop {
}
@RestController
public class OneController {
@GetMapping("/doCheck")
public String doCheck (int age) {
System.out.println("doCheck");
if (age > 1) {
throw new MyException(ExceptionEnu.SUCCESS);
} else {
throw new MyException(ExceptionEnu.FAILD);
}
}
}
记得切面类交给spring管理哦~ @Component
编写切面方法
@Before
这个注解的用法呢,就是说,在执行你要执行的东西之前,执行加了这个注解的方法
比如
@Before(value = "execution (* own.study.web.OneController.*(..))")
public void doAop( ) {
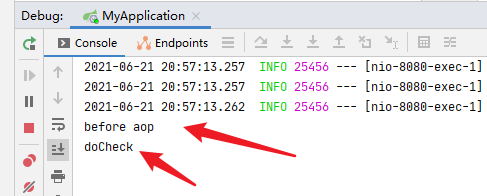
System.out.println("before aop");
}
也就是说,如果我要调用 OneController 的方法,在调用到之前,会执行这个 doAop 方法
让我们来测试一下
@After
这个注解的用法,就是说,当你执行完你的方法之后,真的返回给调用方之前,执行加了这个注解的方法
比如
@After(value = "execution (* own.study.web.OneController.*(..))")
public void doAfter() {
System.out.println("after aop");
}
让我们来测试一下

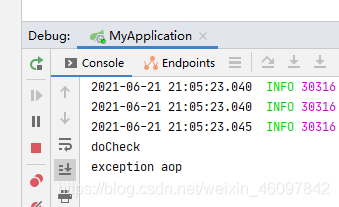
@AfterThrowing
见名知意,在发生异常后,执行加了此注解的方法
注意我上面写的测试方法了吗?我抛出了自定义的异常
让我们测试一下
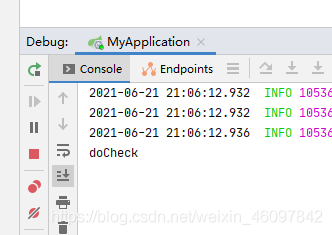
@AfterReturning
这个注解的用法也是看名字就能猜到,执行完后,执行此方法
但是!这个执行完,指的是正常执行完,不抛出异常的那种,不信?我们来试试
@Around
这个是最为强大的一个注解,环绕通知,方法执行前和执行后都会执行加了这个注解的方法
@Around(value = "execution (* own.study.web.OneController.*(..))")
public Object doAround (ProceedingJoinPoint point) throws Throwable {
Gson gson = new Gson();
System.out.println("进入AOP --->" + System.currentTimeMillis());
System.out.println("方法名 = " + point.getSignature().toShortString());
Object result = point.proceed();
System.out.println("响应参数为 = " + gson.toJson(result));
System.out.println("AOP完事了 --->" + System.currentTimeMillis());
return result;
}
@RestController
public class OneController {
@GetMapping("/doCheck")
public Object doCheck (int age) throws InterruptedException {
System.out.println("这个是controller的方法 --->" + System.currentTimeMillis());
Thread.sleep(2000l);
System.out.println("doCheck");
return new MyRsp("1", "success");
}
}

但是,注意!这个环绕通知不是万能的,不是一定好,大家按需要使用,比如一个场景,当你的方法抛出了异常,这个环绕通知就不会再继续执行
我们来实验一下
改写controller的方法
@RestController
public class OneController {
@GetMapping("/doCheck")
public Object doCheck (int age) throws InterruptedException {
System.out.println("这个是controller的方法 --->" + System.currentTimeMillis());
Thread.sleep(2000l);
System.out.println("doCheck");
throw new MyException("1", "success");
// return new MyRsp("1", "success");
}
}
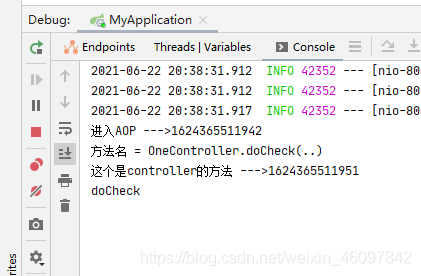
看,AOP后续的没有被执行
以上就是spring的切面,AOP的使用的详细内容,更多关于spring的切面,AOP的使用的资料请关注自学编程网其它相关文章!

- 本文固定链接: https://zxbcw.cn/post/216033/
- 转载请注明:必须在正文中标注并保留原文链接
- QQ群: PHP高手阵营官方总群(344148542)
- QQ群: Yii2.0开发(304864863)
