1.这是一个通过Java反射机制解析的工具类
2.使用时只需创建对应的对象,并在Excel的第一行填上对应的属性名
3.首先要添加相关的jar包:
poi-3.8.jar
poi-ooxml-3.9.jar
poi-ooxml-schemas-3.9.jar
xmlbeans-2.6.0.jar
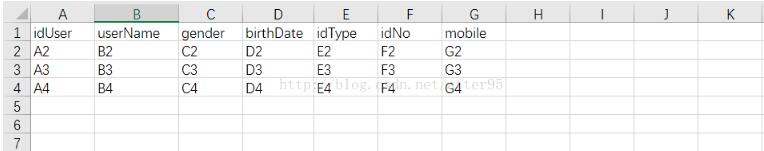
4.看一下Excel的内容:
5.创建对应的实体类:
package com.office.user.dto;
public class UserDTO {
private String idUser;
private String userName;
private String gender;
private String birthDate;
private String idType;
private String idNo;
private String mobile;
public String getIdUser() {
return idUser;
}
public void setIdUser(String idUser) {
this.idUser = idUser;
}
public String getUserName() {
return userName;
}
public void setUserName(String userName) {
this.userName = userName;
}
public String getGender() {
return gender;
}
public void setGender(String gender) {
this.gender = gender;
}
public String getBirthDate() {
return birthDate;
}
public void setBirthDate(String birthDate) {
this.birthDate = birthDate;
}
public String getIdType() {
return idType;
}
public void setIdType(String idType) {
this.idType = idType;
}
public String getIdNo() {
return idNo;
}
public void setIdNo(String idNo) {
this.idNo = idNo;
}
public String getMobile() {
return mobile;
}
public void setMobile(String mobile) {
this.mobile = mobile;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "UserDTO [idUser=" + idUser + ", userName=" + userName + ", gender=" + gender + ", birthDate="
+ birthDate + ", idType=" + idType + ", idNo=" + idNo + ", mobile=" + mobile + "]";
}
}
6.编写工具类:ExcelReader.java
package com.office.poi;
import java.io.File;
import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.lang.reflect.Field;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Map;
import org.apache.poi.ss.usermodel.Cell;
import org.apache.poi.ss.usermodel.DataFormatter;
import org.apache.poi.ss.usermodel.DateUtil;
import org.apache.poi.ss.usermodel.Row;
import org.apache.poi.ss.usermodel.Sheet;
import org.apache.poi.ss.usermodel.Workbook;
import org.apache.poi.ss.usermodel.WorkbookFactory;
import com.office.user.dto.UserDTO;
/**
* Excel 解析工具
*
* @author Neo 2017-5-15
*
* 所需jar: poi-3.8.jar poi-ooxml-3.9.jar poi-ooxml-schemas-3.9.jar
* xmlbeans-2.6.0.jar
*
*/
public class ExcelReader {
private String filePath;
private String sheetName;
private Workbook workBook;
private Sheet sheet;
private List<String> columnHeaderList;
private List<List<String>> listData;
private List<Map<String, String>> mapData;
private boolean flag;
public ExcelReader(String filePath, String sheetName) {
this.filePath = filePath;
this.sheetName = sheetName;
this.flag = false;
this.load();
}
private void load() {
FileInputStream inStream = null;
try {
inStream = new FileInputStream(new File(filePath));
workBook = WorkbookFactory.create(inStream);
sheet = workBook.getSheet(sheetName);
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
try {
if (inStream != null) {
inStream.close();
}
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
private String getCellValue(Cell cell) {
String cellValue = "";
DataFormatter formatter = new DataFormatter();
if (cell != null) {
switch (cell.getCellType()) {
case Cell.CELL_TYPE_NUMERIC:
if (DateUtil.isCellDateFormatted(cell)) {
cellValue = formatter.formatCellValue(cell);
} else {
double value = cell.getNumericCellValue();
int intValue = (int) value;
cellValue = value - intValue == 0 ? String.valueOf(intValue) : String.valueOf(value);
}
break;
case Cell.CELL_TYPE_STRING:
cellValue = cell.getStringCellValue();
break;
case Cell.CELL_TYPE_BOOLEAN:
cellValue = String.valueOf(cell.getBooleanCellValue());
break;
case Cell.CELL_TYPE_FORMULA:
cellValue = String.valueOf(cell.getCellFormula());
break;
case Cell.CELL_TYPE_BLANK:
cellValue = "";
break;
case Cell.CELL_TYPE_ERROR:
cellValue = "";
break;
default:
cellValue = cell.toString().trim();
break;
}
}
return cellValue.trim();
}
private void getSheetData() {
listData = new ArrayList<List<String>>();
mapData = new ArrayList<Map<String, String>>();
columnHeaderList = new ArrayList<String>();
int numOfRows = sheet.getLastRowNum() + 1;
for (int i = 0; i < numOfRows; i++) {
Row row = sheet.getRow(i);
Map<String, String> map = new HashMap<String, String>();
List<String> list = new ArrayList<String>();
if (row != null) {
for (int j = 0; j < row.getLastCellNum(); j++) {
Cell cell = row.getCell(j);
if (i == 0) {
columnHeaderList.add(getCellValue(cell));
} else {
map.put(columnHeaderList.get(j), this.getCellValue(cell));
}
list.add(this.getCellValue(cell));
}
}
if (i > 0) {
mapData.add(map);
}
listData.add(list);
}
flag = true;
}
public String getCellData(int row, int col) {
if (row <= 0 || col <= 0) {
return null;
}
if (!flag) {
this.getSheetData();
}
if (listData.size() >= row && listData.get(row - 1).size() >= col) {
return listData.get(row - 1).get(col - 1);
} else {
return null;
}
}
public String getCellData(int row, String headerName) {
if (row <= 0) {
return null;
}
if (!flag) {
this.getSheetData();
}
if (mapData.size() >= row && mapData.get(row - 1).containsKey(headerName)) {
return mapData.get(row - 1).get(headerName);
} else {
return null;
}
}
/**
* 获取标题
*
* @param eh
* @param maxX
* @return
*/
public List<String> getTitleList(ExcelReader eh, int maxX) {
List<String> result = new ArrayList<String>();
for (int i = 1; i <= maxX; i++) {
result.add(eh.getCellData(1, i));
}
return result;
}
/**
* 获取单行对象
*
* @param object
* @param eh
* @param maxX
* @param titles
* @return
*/
public Object getObject(String className, ExcelReader eh, int y, List<String> titles) throws Exception {
Object bean = Class.forName(className).newInstance();
int length = titles.size();
for (int x = 0; x < length; x++) {
try {
Field field = bean.getClass().getDeclaredField(titles.get(x));
field.setAccessible(true);
field.set(bean, eh.getCellData(y, x+1));
} catch (Exception e) {
System.out.println("没有对应的方法:" + e);
}
}
return bean;
}
/**
* 获取Excel数据列表
*
* @param bean
* @param eh
* @param x
* 每行有多少列数据
* @param y
* 整个sheet有多少行数据
* @param titles
* @return
*/
public List<Object> getDataList(Class<?> clazz, ExcelReader eh, int x, int y, List<String> titles) {
List<Object> result = new ArrayList<Object>();
String className = clazz.getName();
try {
for (int i = 2; i <=y; i++) {
Object object = eh.getObject(className, eh, i, titles);
result.add(object);
}
} catch (Exception e) {
System.out.println(e);
}
return result;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
try {
ExcelReader eh = new ExcelReader("C:\\Users\\Neo\\Desktop\\POI.xlsx", "Sheet1");
List<String> titles = eh.getTitleList(eh, 7);
List<Object> userList = eh.getDataList(UserDTO.class, eh, 7, 4, titles);
for (Object object : userList) {
System.out.println(object);
}
} catch (Exception e) {
System.out.println(e);
}
}
}
6.看一下测试结果:

备注:这是我写于两年前的测试demo,如果生产上有类似需求更建议使用 EasyExcel
补充知识:简单好用-JAVA使用POI解析Excel
相信使用POI的目前已经非常多了,我这边提供一个非常简单便利又通用的POI解析工具类,代码最后有示例代码。可以按照本文直接使用。
import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.io.FileNotFoundException;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStream;
import java.text.DecimalFormat;
import java.text.SimpleDateFormat;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Date;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Map;
import org.apache.log4j.LogManager;
import org.apache.log4j.Logger;
import org.apache.poi.hssf.usermodel.HSSFCell;
import org.apache.poi.hssf.usermodel.HSSFDateUtil;
import org.apache.poi.hssf.usermodel.HSSFRow;
import org.apache.poi.hssf.usermodel.HSSFSheet;
import org.apache.poi.hssf.usermodel.HSSFWorkbook;
import org.apache.poi.poifs.filesystem.POIFSFileSystem;
/**
*
* Title: ExcelReader<br>
* Description: 可以读取xls,xlsx等文件<br>
* Copyright @ 2012~2016 xiaour.github.com<span style="font-size: 1em;"> .All rights reserved.<br></span>
* @author 小鱼儿
* @createDate 2016年8月23日
* @version v1.0
*/
public class ExcelReader {
private POIFSFileSystem fs;
private HSSFWorkbook wb;
private HSSFSheet sheet;
private HSSFRow row;
private static Logger logger = LogManager.getLogger(ExcelReader.class);
private String fileFullPath;
private int sheetNo;
public ExcelReader(String fileFullPath, int sheetNo) {
super();
this.fileFullPath = fileFullPath;
this.sheetNo = sheetNo;
}
/**
* 读取Excel数据内容
* @param InputStream
* @param sheetNo sheet 页号
* @return Map 包含单元格数据内容的Map对象
*/
public List<Map<String,Object>> readExcel() {
logger.info("开始解析xls...");
sheetNo--;//从1开始及从0开始
InputStream is = null;
try {
is = new FileInputStream(fileFullPath);
} catch (FileNotFoundException e1) {
logger.error(e1);
}
Map<String,Object> dataMap = null;
List<Map<String,Object>> dataList= new ArrayList<>();
String value = "";
try {
fs = new POIFSFileSystem(is);
wb = new HSSFWorkbook(fs);
} catch (IOException e) {
logger.error(e);
}
sheet = wb.getSheetAt(sheetNo);
row = sheet.getRow(0);
// 标题总列数
int colNum = row.getPhysicalNumberOfCells();
String[] keyArray = new String[colNum];
for (int i = 0; i < colNum; i++) {
keyArray[i] = getCellFormatValue(row.getCell((short) i));
}
int rowNum = sheet.getLastRowNum();
// 正文内容应该从第二行开始,第一行为表头的标题
for (int i = 2; i <= rowNum; i++) {
dataMap= new HashMap<>();
row = sheet.getRow(i);
if(row!=null){
int j = 0;
while (j < colNum) {
//这里把列循环到Map
if(row.getCell((short) j)!=null){
value = getCellFormatValue(row.getCell((short) j)).trim();
dataMap.put(keyArray[j],value);
}
j++;
}
value = "";
dataList.add(dataMap);
}
}
logger.info("解析xls完成...");
try {
if(is!=null)
is.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
logger.error(e.toString());
}
return dataList;
}
/**
* 根据HSSFCell类型设置数据
* @param cell
* @return
*/
private String getCellFormatValue(HSSFCell cell) {
String cellvalue = "";
if (cell != null) {
// 判断当前Cell的Type
switch (cell.getCellType()) {
// 如果当前Cell的Type为NUMERIC
case HSSFCell.CELL_TYPE_NUMERIC:
case HSSFCell.CELL_TYPE_FORMULA: {
// 判断当前的cell是否为Date
if (HSSFDateUtil.isCellDateFormatted(cell)) {
Date date = cell.getDateCellValue();
SimpleDateFormat sdf = new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy-MM-dd");
cellvalue = sdf.format(date);
}
// 如果是纯数字
else {
// 取得当前Cell的数值
DecimalFormat df = new DecimalFormat("0");
String dfStr = df.format(cell.getNumericCellValue());
cellvalue = dfStr;
}
break;
}
// 如果当前Cell的Type为STRIN
case HSSFCell.CELL_TYPE_STRING:
// 取得当前的Cell字符串
cellvalue = cell.getRichStringCellValue().getString();
break;
// 默认的Cell值
default:
cellvalue = " ";
}
} else {
cellvalue = "";
}
return cellvalue;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
List<Map<String, Object>> dataList;
// 对读取Excel表格标题测试
ExcelReader excelReader = new ExcelReader("D:\\okcoin-2016-08-3XZS.xls",1);
dataList = excelReader.readExcel();
for(Map<String,Object> theMap:dataList){
System.out.println(theMap);
}
}
}
这个类导入相应的jar之后就可以用了哦。
以上这篇Java通过反射将 Excel 解析成对象集合实例就是小编分享给大家的全部内容了,希望能给大家一个参考,也希望大家多多支持自学编程网。

- 本文固定链接: https://zxbcw.cn/post/193525/
- 转载请注明:必须在正文中标注并保留原文链接
- QQ群: PHP高手阵营官方总群(344148542)
- QQ群: Yii2.0开发(304864863)
